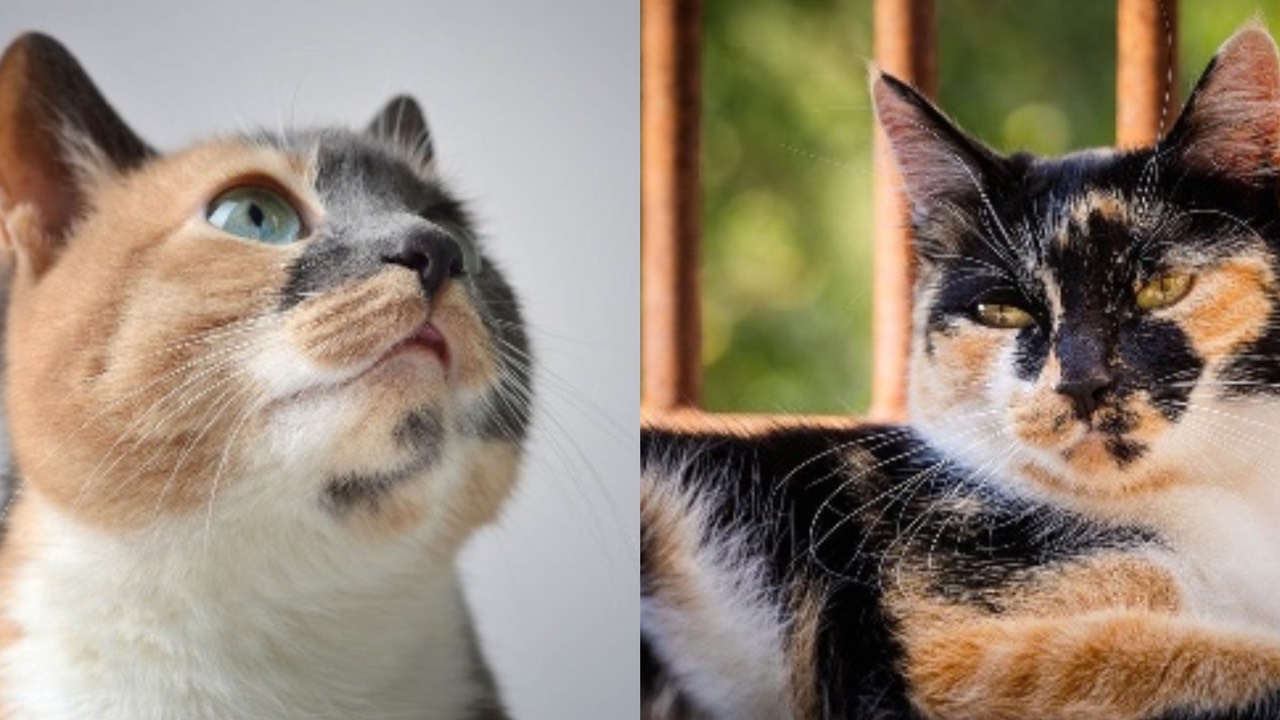
Calico refers to a colour pattern that is common in random-bred and purebred cat populations. The term ‘calico’ refers to a tri-colour coat that consists of white, black and orange, white, chocolate and red or white, blue (grey) and cream in its dilute form.
In calico cats, the red or cream patches always exhibit a tabby pattern, characterised by distinct stripes, spots, or swirls. In contrast, the secondary colour, whether black or blue, appears in a solid, non-tabby form.
The calico pattern is linked to the X chromosome. The black, orange, blue, and cream are produced by two genes located on the X chromosome. A female cat has two X chromosomes (XX), allowing her to display both black and orange colours, along with white which is dictated by a separate ‘white spotting’ gene. Male cats, with their XY chromosomal structure, generally have only one of these colours along with white, since they have just one X chromosome. However, some rare male calicos exist; these cats usually have an extra X chromosome (XXY), a condition known as Klinefelter syndrome.
Different types of calico cat
Dense calico

This is the classic calico cat most of us know. The pattern consists of patches of white, black and red and is commonly found in mixed-breed and purebred cats. As noted, the red is always tabby, while the second dense colour is solid. On a side note, if the second colour was also tabby, the cat would be a caliby and not a calico.
Dilute calico

The dilute calico coat is made up of patches of cream, blue and white. Dilution is recessive to dense, which means the cat must have two copies of the dilute gene (one from each parent). Melanin synthesis is normal in the dilute cat, however, the pigment granules are enlarged and deposited unevenly in the hair. The result is clumps of melanin in varying sizes along the hair shaft and areas that lack pigment, producing the illusion of a lighter coat colour.
Van calico

Image credit, Inkeri Satala, Flickr
The van calico is characterised by its limited calico markings primarily on the head and tail, while the majority of the body remains white. This pattern is reminiscent of the traditional “Van” markings commonly associated with the Turkish Van breed although it can occur in some other breeds and random-bred cats.
The van pattern occurs when the cat inherits two copies of the white spotting gene, leading to widespread white on the body, with small patches of fur on the head and tail.
Harlequin calico

Harlequin cat refers to a specific coat pattern in cats where the body is primarily white but with large patches of colour. The term “harlequin” is often used in various animal breeds to describe a similar pattern of alternating colour and large areas of white.. In cats, this harlequin pattern is a variation of the piebald or white spotting effect.
Shorthaired calico

Shorthaired cats are more prevalent than their longhaired counterparts. The genetic underpinnings lie in the inheritance patterns of fur length in cats. Specifically, the gene responsible for fur length has two main alleles: one for short hair and one for long hair.
The allele for shorthaired fur is dominant, denoted by “L“, while the allele for longhaired fur is recessive, represented by “l“. This means that for a cat to have long hair, it must inherit two copies of the recessive allele (ll). If a cat inherits at least one dominant shorthaired allele (L), it will have short hair, regardless of the second allele. This can result in combinations like LL (homozygous dominant) or Ll (heterozygous), both producing shorthaired cats.
Longhaired calico

Curly coated calico

Curly-coated cat breeds, like the Selkirk Rex, Devon Rex, and Cornish Rex, stand out due to their distinctive wavy or curly fur, a result of specific genetic mutations. These breeds often possess soft, plush coats, which may be short or long. While the curliness of their fur is a defining feature, these cats can come in a variety of colours and patterns, including calico.

Hairless calico

Hair length in cats can vary from longhaired to hairless. While we do use the term hairless, most of these breeds have a peach-like fuzz which feels like chamois. Hairless breeds include the Sphynx, Don Sphynx, Peterbald and Ukrainian Levkoy.
The hairless gene can vary between breeds, in some, such as the Sphynx, the gene is recessive, and the offspring must inherit a copy of the hairless gene from both parents. The gene responsible for the hairlessness in the Donskoy is dominant and only one copy is necessary for offspring to inherit the trait. All coat colours are permitted in hairless cat breeds, including calico.
Male calico

Male calicos are extremely rare, and the often-cited statistic suggests that approximately 1 in 3,000 calico cats are male, although this number can vary depending on the source.
Most male calico cats are sterile due to their atypical chromosomal pattern. The male calico typically has an XXY configuration instead of the typical XY configuration seen in most male mammals. Most male cats with this chromosomal pattern are sterile, due to abnormalities in the development of the testes and reduced testosterone production.
What breed is a calico cat?
Calico refers to a coat pattern rather than a specific breed. Many different breeds can produce calico-patterned cats. While some variations, such as the “harlequin” or “van,” may suggest specific visual arrangements, the underlying genetics are more about colour distribution than breed delineation. This genetic diversity allows for an array of cats, from various breeds, to proudly wear the enchanting calico design.
Is my cat a calico or tortoiseshell?

All calico cats are characterised by predominantly white fur punctuated with large, irregular patches of the classic calico colours: black, orange, grey (blue) and cream or chocolate and cream. The tortoiseshell coat is made of two colours, black and red, blue and cream or chocolate and cream. There is no white.
Conclusion
- Calico is a coat pattern that is made up of three colours, white, red or cream with black, chocolate or blue.
- The red or cream patches are always tabby, as the non-agouti (a/a) or hypermelanistic gene, which overlays the agouti base colour with melanin pigment to produce a solid-coloured cat does not affect phaeomelanin (red). The second colour of black, brown or blue is always solid and does not contain a tabby pattern. If the second colour is tabby, the cat is a caliby, not a calico.
- Calico cats are almost exclusively female.
- The calico pattern is widespread in both the purebred and random-bred communities.
- Calico is a symbol of good luck or wealth in Asian countries.